Basics of Motion in a Plane
Basics of Motion in a Plane: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, 2D Motion, Multiplication of Vectors, Condition for Two Vectors to be Parallel & Calculation of Angle Between Two Vectors Using Vector Product etc.
Important Questions on Basics of Motion in a Plane
A body of moves in the plane under the action of a force given by Assuming that the body is at rest at time the velocity of the body at is:
A bus is moving on a straight road towards north with a uniform speed of turns through anticlockwise. If the speed remains unchanged after turning , the increase in the velocity of bus in the turning process is:
The position vector of a particle is The velocity of the particle is:
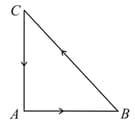
Three forces starts acting simultaneously on a particle moving with velocity These forces are represented in magnitude and direction by the three sides of a triangle (as shown). The particle will now move with velocity
The trajectory of a projectile in a vertical plane is where are constants, and and are respectively the horizontal and vertical distances of the projectile from the point of projection. Find the maximum height attained by the projectile and the angle of projection from the horizontal.
A ball is projected from ground with at with horizontal. A wall is of height at distance of from the projection point. The ball will hit the wall at height of
A vector in plane makes an angle of with -axis. The magnitude of -component of vector is . The magnitude of -component of the vector will be :
When vector is subtracted from vector , it gives a vector equal to . Then the magnitude of vector will be:
Two forces having magnitude and are perpendicular to each other. The magnitude of their resultant is:
If and then find the displacement from A to B

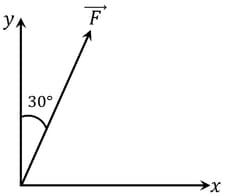
If y-component of a force acting in x-y plane is . Then the x- component will be
Two forces of magnitude and act perpendicular to each other. The magnitude of the resultant force is equal to
If momentum of a particle is given by
a) Find the magnitude of force at any time.
b) Find the angle between momentum and force.
The projection of the vector on the directed line , if angle will be
If and . The magnitude of component of vector along vector will be _____
The resultant of two vectors is perpendicular to one of them and has the magnitude . If the sum of the magnitude of two vectors is then their respective magnitude are
An aeroplane has to reach to and back again along straight line. The speed of aeroplane with respect to wind is . The wind blows perpendicular to line with speed . The distance between and is . The total time for the round trip is
Four particles lie initially at the corners of a square of side length. All the particles start to move with speed moves towards , moves towards , moves towardsand moves towards . The distance covered by a particle till they meet, is